[ad_1]

Mike Hotchkiss, Raspberry Shake
On the afternoon of January 12, 2010, a magnitude-7.0 earthquake struck about 16 miles west of Haiti’s capital of Port-au-Prince. Among the many most vital seismic disasters recorded, greater than 100,000 folks misplaced their lives. The harm—costing billions of {dollars}—rendered greater than 1,000,000 folks homeless and destroyed a lot of the area’s infrastructure. The earth tore on the comparatively shallow depth of about 8 miles, toppling poorly constructed buildings.
On the time, Haiti had no nationwide seismic community. After the devastating occasion, scientists put in costly seismic stations across the nation, however that instrumentation requires funding, care, and experience; right now, these stations are not practical. In 2019, seismologists opted to strive one thing completely different and much cheaper—citizen seismology by way of Raspberry Shakes.
On the morning of August 14, 2021, amidst a summer time of COVID-19 lockdowns and political unrest, one other earthquake struck, offering the chance to check simply how helpful these Raspberry-pi powered gadgets may very well be. In a paper revealed on Thursday in Science, researchers described utilizing the Raspberry Shake information to show that this citizen science community efficiently monitored each the mainshock and subsequent aftershocks and offered information integral to untangling what turned out to be a less-than-simple rending of the earth.
Extra highly effective earthquake
The August 2021 occasion clocked in with a magnitude of seven.2—40 p.c extra highly effective than its 2010 predecessor. It ruptured alongside the identical fault zone however in a extra rural area, leading to comparatively fewer losses. However, about 2,500 folks misplaced their lives, 13,000 have been injured, and not less than 140,000 homes have been destroyed or broken.
One of many Raspberry Shakes put in in 2019 occurred to be sited about 21 kilometers from the epicenter, with two extra citizen stations close to sufficient to detect the quake. Together with two different seismic stations in Port-au-Prince—one on the US embassy and one other academic instrument in a neighborhood highschool—the Raspberry Shake notification got here via inside a minute of the earthquake, stated Eric Calais. (Calais was among the many scientists main the worldwide response after each the 2010 and 2021 earthquakes and a pacesetter of the citizen science initiative.) Two extra Raspberry Shakes close to the epicenter, unavailable throughout the primary shock due to Web connectivity points, have been reconnected by their hosts inside two hours.
A less-than-useful community
To detect any rumblings within the floor—together with earthquakes—you want a seismic station full of sensors, a way to file the information, a spot to retailer that info, and energy to run the entire contraption. Seismologists sometimes depend on costly seismic stations that have to be rigorously put in to reduce background vibrations attributable to folks, wind, and even atmospheric stress adjustments. To report information in actual time, stations want fixed communication by way of mobile networks or satellite tv for pc hyperlinks. These stations have to be maintained by specialists educated particularly for this function.
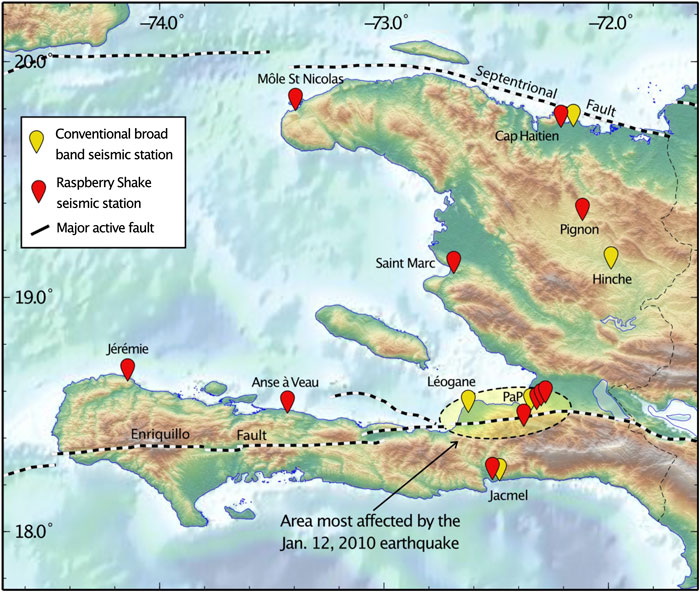
The Raspberry Shake community in Haiti.
After the 2010 earthquake, the newly put in typical seismic community was to be maintained by Haiti’s Bureau of Mines and Vitality. By 2018, when a magnitude-5.9 earthquake killed 17 folks, none of those stations was practical, forcing Haiti’s inhabitants to depend on info gathered remotely by the US Geological Survey.
Based on coauthor and seismologist Anthony Lomax, his impression from Haitian scientists is {that a} main obstacle to a steady seismic community is normal lawlessness, starting from theft of apparatus to ransom kidnapping.
“The three principal roads out of Port-au-Prince to the provinces are managed by gangs,” agreed Calais. “The federal government needed to pay them to cease taking pictures and robbing in order that humanitarian assist might undergo after the quake.”
Raspberry Shake to the rescue
Raspberry Shakes—low-cost plug-and-play seismic stations that require little upkeep—can circumvent most of the issues plaguing the traditional seismic community. Backed by a Raspberry Pi pc that manages the add of information to servers, Raspberry Shakes want an Web connection and wall socket to supply information storage and energy, respectively. Whereas typical seismic stations can price nicely over $10,000 every, these devices are a fraction of that: about $400.
Though a number of fashions exist that may measure various things (like this Raspberry Shake and Increase, which additionally consists of an infrasound detector), the scientists accountable for deploying Haiti’s citizen science community opted for the Raspberry Shake 4D, which features a vertical velocity detector and accelerometers that measure motion in two horizontal instructions in addition to up-down. Funding for this venture comes primarily from two French institutes, stated coauthor Françoise Courboulex. The Raspberry Shake community was principally put in throughout Haiti by Steeve Symithe and Calais.
Symithe, Calais, and their fellow citizen scientists positioned stations in handy places, just like the above-mentioned dwelling rooms, which tended to be slightly noisy locales. Ambient vibrations picked up by these stations are sometimes a lot greater than a standard seismic station that’s shielded from the tremblings of on a regular basis life by specifically designed vaults. Despite the noise, these Raspberry Shakes nonetheless present useful info in a rustic missing different seismic instrumentation.
At present, many stations present information in actual time, out there on the ayiti-seismes platform. This community can detect a lot smaller magnitude earthquakes in Haiti than different Caribbean regional networks, with the most recent places and magnitudes out there on the web site.
Shake check
The Raspberry Shake station nearest to the earthquake, R50D4, offered invaluable info each throughout and after the earthquake. First, the height floor acceleration—the utmost acceleration the bottom skilled throughout an earthquake on the location of that seismic station—was barely larger than anticipated. The anticipated worth went into constructing codes revealed in 2012. Acceleration and shaking, stated Lomax, are sometimes larger on greater flooring. This means that newer, multistory buildings weren’t designed to face up to the 2021 occasion.
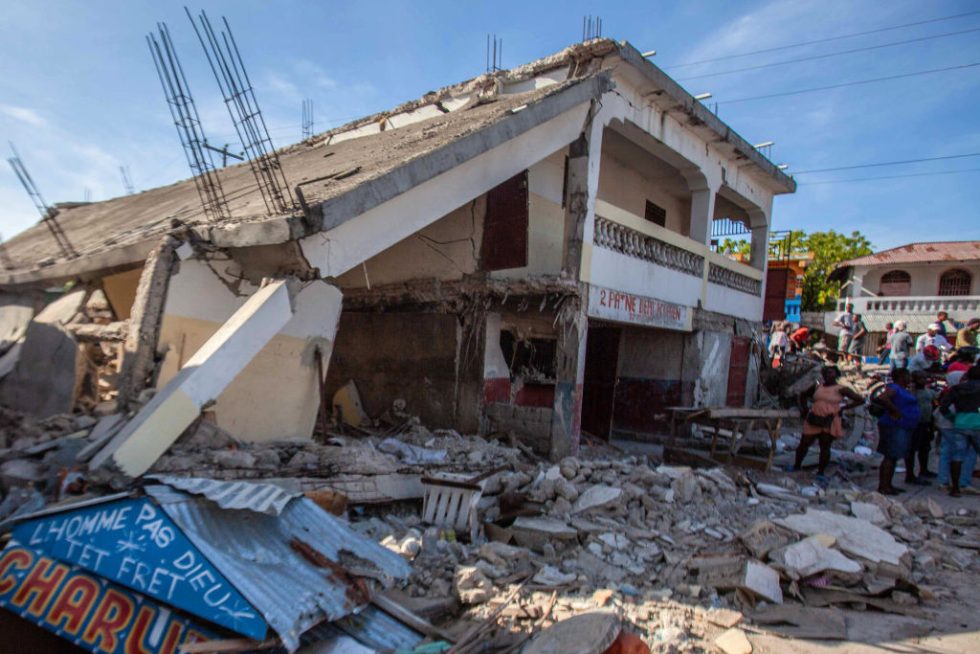

In any case, solely about lower than 10 p.c of Haitian buildings are designed and verified by engineers, stated Calais. “It’s as much as the engineers to observe the code, or not,” he defined. “There isn’t a legal responsibility.”
The one well-located station, R50D4, additionally offered seismologists the chance to check whether or not they might use machine studying to determine aftershocks utilizing solely a single seismic station. They educated the algorithm to detect earthquakes larger than magnitude-3.0 utilizing databases of earthquakes and noise. This machine-learning process utilized to station R50D4 gave the time and approximate magnitude for any subsequent aftershocks close to the station, stated Lomax.
The ensuing catalog in contrast extremely nicely with the catalog of aftershocks produced by the complete citizen seismic community. “AI is kind of highly effective at discovering alerts hidden within the noise, offered the algorithm has been correctly educated to acknowledge earthquakes,” stated Calais.
This examine highlights the significance of observations close to the location of rupture, stated seismologist Wenyuan Fan, who was not concerned on this examine. “Even sparse, low-cost, comparatively noisy observations might support hazard mitigation and threat administration.”
Clusters of slip, clusters of quakes
One of many different issues the Raspberry Shake information offered info on is the sophisticated nature of the fault system in Haiti. The fault on which the 2010 and 2021 earthquakes struck appears to primarily be strike-slip, by which two tectonic plates grind previous one another as a substitute of transferring towards or away from each other. However in Haiti, the Caribbean plate scrapes towards the North American plate whereas additionally pushing towards it. This indirect motion signifies that earthquakes might be each strike-slip, whereas additionally having a reverse element, by which they arrive collectively, right here at an angle. These reverse faults cover underground, and in contrast to strike-slip faults, might by no means broach the floor whereas wreaking havoc from beneath.
The 2010 earthquake contained components of each these kind of plate movement, and evaluation of seismic information suggests the identical occurred in 2021.
Based mostly on their evaluation, which incorporates each Raspberry Shake information and data from typical seismic stations positioned at a distance, Calais and his colleagues discovered that the 2021 earthquake may very well be break up into two separate sub-events. The earthquake started as a thrust, by which one facet moved up relative to the opposite, however this was principally hidden—this a part of the earthquake didn’t breach the floor. The second sub-event was the strike-slip element that occurred west of, and after, the primary half. This rupture was shallower and broke the floor, in accordance with Calais.
The thrust-sub occasion might have “triggered” the strike-slip one. That they’re merely coincidence is almost unattainable, stated Lomax.
“Extra work will inform us,” stated Calais, what the connection is between these two elements of the entire earthquake. “The earthquake might have stopped after sub-event one, however the rupture carried sufficient vitality to leap to a different close by section,” he stated, “identical as 2010!”
Science, 2022. DOI: 10.1126/science.abn1045
Alka Tripathy-Lang is a contract science author with a Ph.D. in geology. She writes about earthquakes, volcanoes, and the interior workings of our planet.
[ad_2]

