[ad_1]
Garmin seems to have included ECG performance inside their just lately launched Venu 2 Plus smartwatch, albeit with out acknowledging its existence or together with the function at launch. That is notable as a result of there’s at present no Garmin wearable with ECG performance on it, properly, not less than formally anyway. Nonetheless, Garmin’s shift in direction of medical units and particularly ECG performance wouldn’t essentially be a shock. Final spring, Garmin quietly started a medical trial (2021) to check ECG-related options “derived from a Garmin wrist-worn, client system”.
The presence of ECG diagnostics {hardware} and diagnostics app on the Venu 2 Plus, mixed with Garmin’s medical trials testing, signifies the corporate is clearly working in direction of a purpose of launching ECG performance of their wearables. In fact, the timing of that’s nonetheless unknown – in addition to whether or not or not the Venu 2 Plus will *ever* formally acquire ECG performance.
When the corporate launched the Venu 2 Plus this previous January, its core new options have been a speaker/microphone, with calling-related capabilities. Omitted from that listing, was any point out of ECG performance – and even future ECG performance. The truth that we’re seeing it now’s largely attributable to a seemingly unintended act that left it within the diagnostic menus on items that have been produced previous to February. Garmin has since eliminated that diagnostic menu in a firmware replace, although it’s extremely uncertain they’ve eliminated the precise ECG {hardware}.
At current Garmin doesn’t formally acknowledge its existence within the unit (extra on that later within the submit), however does acknowledge the medical research. In fact, it kinda has to acknowledge that because it’s listed underneath their title on the US Authorities web site. However once more, we’ll circle again to that later within the submit.
First Take a look at Garmin’s ECG:
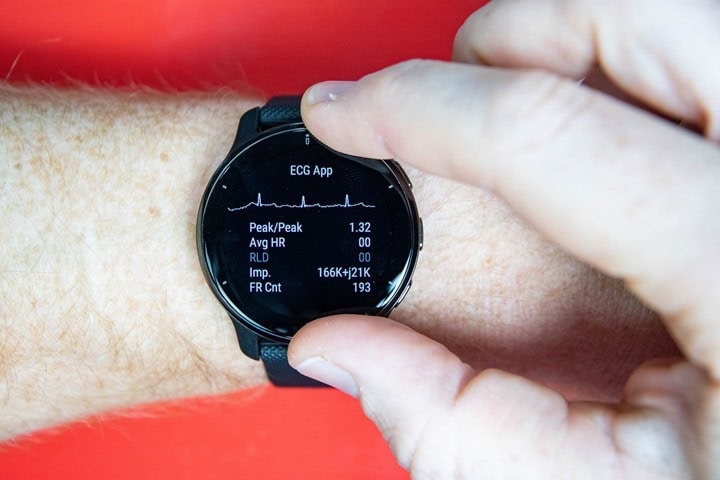
The power to see the ECG perform is hardly a completed product. To be clear – all the things you see on this submit is the {hardware} take a look at/diagnostics menu inside the watch. This menu is often reserved for Garmin technicians to troubleshoot numerous options. It contains diagnostic pages for sensors, accelerometers, NFC performance, WiFi, Bluetooth, GPS, shows, and so on… Usually talking, for those who’re utilizing that menu – one thing has gone incorrect and also you’re making an attempt to find out whether or not the {hardware} is the trigger. It’s obtainable on each Garmin watch and has been for in all probability a decade now.
Nonetheless, what’s not been there’s a new ECG diagnostic web page. That was by chance found by a person on the Garmin Boards again in early February. Nonetheless, their expertise there was short-lived, with none additional documentation or images. After they went again to entry that function later within the day, it was now not there. That’s as a result of, by that time, the watch had up to date its firmware to the latest model, which meant the choice went away (it seems firmware model 8.05 in late January eliminated it – previous to the Garmin Discussion board submit).
You see, Garmin, like most firms, manufactures {hardware} properly earlier than merchandise begin transport to you. Apple, GoPro, and numerous others do the identical. It permits them to stockpile {hardware} whereas they finalize the software program. That is usually 2-4 months forward of launch. When these items are made, they want some form of software program on them in order that if you unbox them for the primary time, they’ll pair as much as your cellphone and get up to date to the present firmware. Mockingly, I simply posted about this idea a number of days in the past.
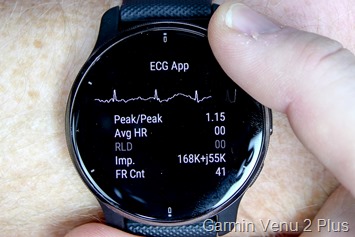
Given my present Venu 2 Plus had lengthy since up to date to the latest manufacturing firmware and eliminated the function, I did what any regular particular person would do – I ordered one other new Venu 2 Plus off of Amazon, and it arrived the subsequent day. I then opened it up and with out pairing to something, went into the diagnostics menu. It confirmed the factory-made firmware model of 6.05 – so lots previous to nonetheless include the function. And certain sufficient, simply two faucets by the menu pages later was the ECG diagnostic menu:
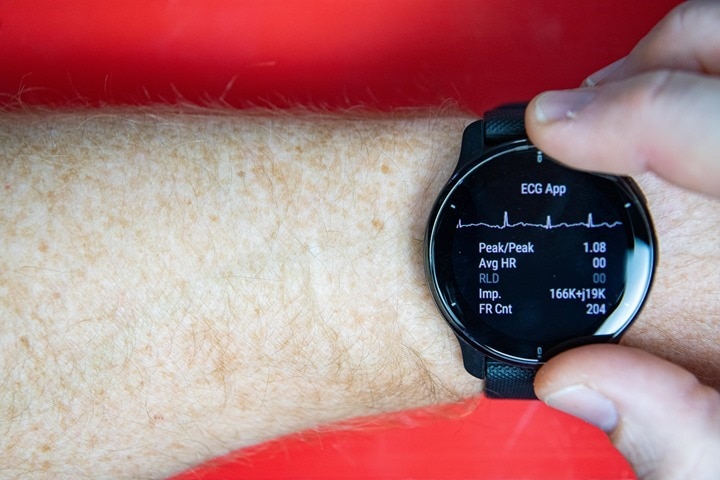
Now to reiterate once more, this isn’t meant to be a fairly show of your ECG. It’s a {hardware} diagnostic take a look at display, so it’s displaying the core information that Garmin must troubleshoot/take a look at the ECG {hardware} itself. Undoubtedly, the traditional end-user function can be prettier and have fairly purple ECG strains, warnings, utilization directions, and extra. Why purple strains? As a result of clearly, it needs to be purple. Some other colour means it’s clearly faux.
The way in which the ECG app works is that you simply place your reverse thumb and index finger on the bezel, and inside about 1-2 seconds it’ll begin studying your ECG – taking a number of extra seconds to stabilize. The second you take away your fingers from the bezel, it stops. That is basically the identical as how different firms have applied it. With some firms (like Apple), you contact the digital crown as a substitute, however the idea is identical. By utilizing your reverse wrist/hand, you full the required electrical circuit.
Enjoying round with hand place seems to comparatively simply affect accuracy, as does enjoying round with one finger versus two fingers on the bezel. Actually, this diagnostics software program is probably going 5-7 months previous, and was by no means meant to do something greater than present uncooked sensor information. Similar to all the opposite service menu pages do, for issues like accelerometer, coronary heart fee, Bluetooth, WiFi, GPS, and extra.
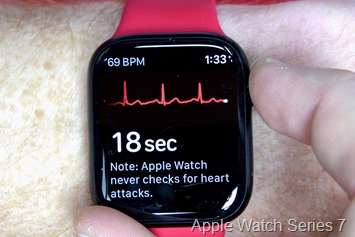
Nonetheless, it’s clearly producing a valid-looking ECG. And provided that Garmin accomplished a 568-person medical trial final October with not less than some Garmin-made ECG {hardware}, it’s doubtless by this level Garmin is aware of what they’re doing right here. Right here’s a have a look at how that ECG wave sample appears to be like in comparison with an Apple Watch Collection 7, worn again to again (one after one other):
Now usually, most watches that function ECG performance additionally permit you to document the ECG hint after which export the outcomes to ship to a physician. Additionally they sometimes monitor/verify for sure situations, like atrial fibrillation, which is an irregular heartbeat sample. They NEVER verify for whether or not a coronary heart assault is happening.
Nonetheless, given that is within the diagnostics menu and never the traditional function, we don’t get that right here. Undoubtedly, that’d be in any regular ECG function down the street (as a result of it’d be pointless with out it), so we’ll need to see on that – if and when Garmin makes a function out of this. And in reality, in Garmin’s medical trials they even define what options they’re making an attempt to finish. So, let’s dig into that.
The Scientific Trials Research:
Final Spring Garmin recruited for a US medical trial. As by legislation, any medical trial within the US that’s achieved on folks have to be registered and listed publicly on the ClinicalTrials.gov database/web site. That authorities group isn’t fairly the FDA, however has unfastened ties to it. It’s these medical trials which might be then used as the premise for submission to regulatory businesses just like the FDA (within the US), or different medical regulatory our bodies world wide. Garmin’s submission is right here.
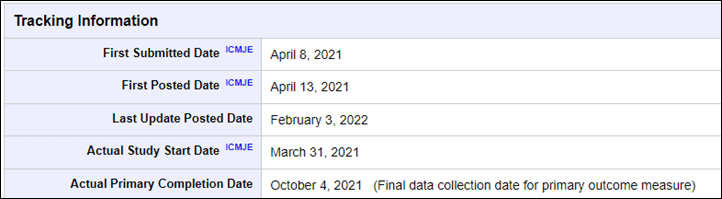
In Garmin’s case, they started the research final March thirty first, 2021, after which concluded the response interval on October 4th, 2021. That implies that throughout that timeframe they have been actively gathering information from real-world people. Then final month (February 2022), they filed an replace to the research indicating they did certainly conclude information assortment final fall, in addition to the ultimate variety of members.
In Garmin’s case, that they had initially filed the trials to incorporate 460 members, nevertheless, by the tip, that they had included 568 members. In speaking to varied trade people, that’s fairly regular, as members that have been initially included are sometimes faraway from the research afterward. That may be as a result of the person may not have met the standards (extra on that in a second) upon additional inspection, or maybe there have been protocol errors of their pattern. You’d anticipate to see some enhance between the projected quantity and the ultimate quantity.
The research’s objective was, in their very own phrases:
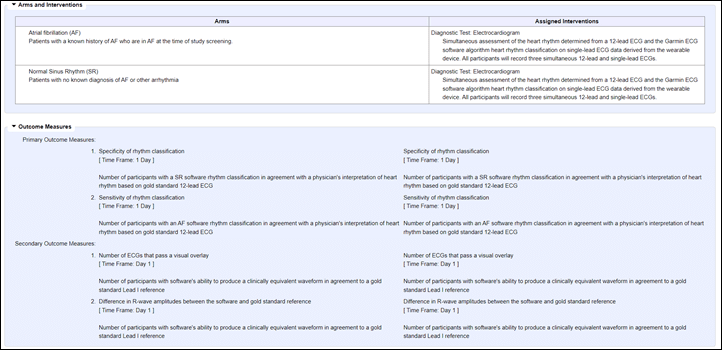
“to verify the Garmin ECG (electrocardiogram) software program algorithm can detect and classify atrial fibrillation and regular sinus rhythm on single lead ECG information derived from a Garmin wrist-worn, client system. The research may also affirm the software program’s means to create a Lead I ECG that’s clinically equal to a reference system. The Garmin ECG software program will not be a diagnostic system and is meant for informational functions solely.”
In different phrases, they wished to:
A) Validate the accuracy of the ECG information itself
B) Validate the accuracy of their software program figuring out atrial fibrillation and a standard sinus rhythm
Principally, they have been aiming to have the identical baseline validation and options that Apple, Samsung, and others do.
In an effort to do that, because the research outlines, they recruited by their associate analysis/medical organizations two totally different teams of individuals. These with identified AFib (atrial fibrillation), and people with a standard sinus rhythm. And so they did this throughout 6 totally different websites within the US. It’s this two-group recruitment that may result in variations within the last projected quantity, when for instance somebody says they’ve AFib, however upon doing a reference ECG with a physician throughout the trial, they really don’t. Thus, extra members need to be recognized.
The research’s execution was achieved by six totally different websites, although a few of them are a part of the identical group.
A) Hope Analysis Institute (Phoenix, AZ)
B) MedStar Washington Hospital Middle (Washington DC)
C) HealthEast (St. Paul, MN)
D) Northwell Well being North Shore College Hospital (Manhasset, NY)
E) Northwell Well being Lenox Hill Hospital (New York, NY)
F) MedStar Well being Cardiac Electrophysiology at Fairfax (Fairfax, VA)
Garmin themselves after all commissioned the research, and particularly, their well being division. I assumed it was notable that the appliance really listed the names and titles of the Garmin folks in control of it. That itself wasn’t notable, however fairly the truth that Garmin now really has somebody with a job title of “Scientific Analysis Supervisor” was fascinating (and her background at different organizations over the previous decade is tremendous fascinating in microbiology R&D in addition to managing different medical trials and analysis). This is sensible, provided that Garmin must have folks with expertise in these fields. Different names listed on the research even have expertise in these areas.
The preliminary research paperwork do define their precise protocol for every take a look at participant:
In a nutshell, the research collects information from a reference system, then collects information from a Garmin watch. Then they’re trying to perceive whether or not or not the software program accurately predicts the rhythm classification (AFib or regular). They’re additionally taking a look at secondary outcomes that validate that the beautiful graph that you simply see is definitely medical-worthy and that a physician taking a look at it may possibly accurately determine the rhythm classification. Lastly, they’re wanting to make sure that the R-Wave (the spike inside the fairly graph) matches that of their reference system.
At this level, Garmin has till later within the 12 months to submit the ultimate outcomes of that research to the federal government. At current they haven’t uploaded that, which is regular. Most tech firms on this ECG area don’t sometimes add these last outcomes till they acquire FDA approval.
Nonetheless, the truth that they up to date the official file although on February third, 2022, clearly signifies issues aren’t lifeless right here. Trying on the timeframe for the research, it was a bit longer than Apple’s was for his or her research (take note Apple did this in 2018, pre-covid, which undoubtedly would have slowed down many features of this). Each firms had about the identical variety of folks within the research, and the identical variety of websites (the truth is, even sharing some websites/organizations).
Have in mind although, the conclusion of the data-gathering part again in October (for Garmin) is merely one step in a protracted street to FDA certification. In Apple’s case, their FDA certification took about 5-6 months after their research “main completion date”. And once more, it’s onerous to reiterate the affect of COVID on delays to all processes right here in 2022 versus 2018.
Going Ahead:
That in the end will get to the massive query: Is an ECG function coming to Garmin watches, or the Venu 2 Plus particularly? Properly, it’d actually appear that Garmin has been lining up their geese for that to happen. Between the medical research final summer time, the latest research submitting doc updates, and now the {hardware} clearly being contained in the Venu 2 Plus – these are robust indicators.
However there are additionally the explanation why it might by no means seem within the Venu 2 Plus. First, it’s totally believable that the ECG elements, or design of such, that Garmin put within the Venu 2 Plus didn’t meet their high quality or accuracy ranges for ECG. Whereas that appears unlikely at that time, it’s actually a situation.
The ECG perform right here is classed as a medical system (underneath the FDA’s Software program as a Medical Gadget program), so it required approval by the FDA and comparable organizations. Moreover, it sometimes requires that on a per-country foundation. Some international locations have their very own our bodies (e.g. the US), some have a central certifying physique shared between international locations (like within the EU), and a few international locations will merely comply with certification by the US or EU. As we noticed with Apple, Samsung, and others – these have been a staged rollout, nation by nation. And a few international locations by no means obtained it, as a result of the burden of getting medical system approval in a given nation might not have been well worth the effort for the variety of units in that nation.
So, armed with all this curiosity, I merely requested Garmin. Right here’s what Mary Woodbury, Garmin’s PR lead for his or her Wellness merchandise/division (which the Venu collection falls underneath) needed to say:
“Garmin has carried out a medical trial to evaluate the aptitude of our smartwatches to precisely detect the presence of AFib. The small print of the research could be discovered on clinicaltrials.gov”
Which..is all they might say. They’d not present any remark concerning the existence of ECG options within the system itself – solely confirming the medical trial that existed. Their lack of remark can be according to US FDA laws that prohibit firms from discussing medical units till FDA approval has been granted. Within the case of Apple for instance – they waited till that they had precise approval from the FDA earlier than asserting that ECG performance can be coming to watches (though there was one other hole between the announcement of existence and implementation on shoppers’ wrists). Whereas Withings, a French firm, didn’t initially search US FDA approval and thus pre-announced a 12 months previous to the precise availability of the function.
Keep in mind, as superior as Garmin is inside the sports activities tech realm, they’re a tremendously fiscal and legally conservative firm. They nearly by no means pre-announce options. And in the previous couple of years, they’ve shifted to not asserting merchandise till they will ship instantly (versus asserting one thing coming in a number of months). Them even acknowledging the existence of the ECG function of this is able to land them in sizzling water with the FDA. Undoubtedly, quite a lot of four-letter phrases occurred in Kansas again in January after they realized this diagnostics menu was left in there.
Nonetheless, on this case, their acknowledgment isn’t actually mandatory. They’ve acknowledged the medical trial to detect AFib with an ECG in a Garmin wearable, and so they’ve by chance demonstrated that the Venu 2 Plus has succesful {hardware}. The one issues left to know are when and the place. When will Garmin announce it, and to which nation will or not it’s obtainable? In fact, there’s nonetheless the “if” issue. It’s totally believable that Garmin doesn’t request/obtain FDA approval for this iteration. Thus, we might by no means see ECG on the Venu 2 Plus and positively, I wouldn’t purchase the Venu 2 Plus with that as a purpose, since no promise (and even trace) has ever been made in that realm.
With that, thanks for studying!
[ad_2]