Within the final article on this collection, Superior Git Aliases, we took a take a look at some superior aliases for Git. Nonetheless, the true energy of Git aliases comes from writing customized scripts. These help you construct Git instructions that may do something you possibly can think about.
On this article, I am going to present you how one can create script aliases with Git. We’re going to try a number of superior scripts you should utilize for Git which can be tremendous helpful and can prevent a bunch of time.
Script Aliases
We’ll be utilizing Bash for our scripts. Bash is an unsightly language, but it surely has the good thing about working virtually wherever. To your personal scripts, you should utilize any scripting language you would like.
In case you’re not accustomed to Bash scripting, do not panic! Whereas a number of the syntax could look funky, you possibly can largely muddle your manner via. (That is not one thing you sometimes hear from a coding article, proper?) I like to recommend studying Be taught Bash in Y Minutes and rifling via Google or Stack Overflow for something that does not make sense.
Step one is to create a file to your script. I wish to retailer these recordsdata in my Dotfile’s bin listing, however you possibly can put them wherever you would like in your pc. Simply be sure it is someplace simple to recollect.
contact bin/git/git-example
Subsequent, you will want so as to add some boilerplate to the highest of your script.
#!/usr/bin/env bash set -euo pipefail
The primary line is named a shebang), and it tells your pc that the file is a script that needs to be run with Bash. This particular runs the script with Bash. To make use of a unique language, substitute bash for one thing else, like ruby or python3.
The second line tells bash to exit if there are any errors, undefined variables, or errors in a pipeline. I do not know why this is not the default in Bash, however not less than it is simple to arrange with this line.
You possibly can run your script as-is with (bash bin/git/git-example), however who has time to write down out bash each time they wish to run one thing? As an alternative, make your script executable.
chmod +x bin/git/git-example
Now you possibly can run your script with out prepending bash to it (e.g. bin/git/git-example).
Lastly, it’s best to add your script to Git’s aliases. Substitute the trail to your script beneath.
[alias] instance = "!$HOME/.dotfiles/bin/git/git-example"
That is it! Now you possibly can run git instance to run a script that does not do something!
Listing All Branches
By default, if you run git department, you get the branches you might have saved domestically. However what if you wish to see all of the branches out there to you? You possibly can obtain this by including the --all flag to your branches.
git department --all
I wish to package deal this right into a git-branches script and add just a few extras to it.
#!/usr/bin/env bash set -euo pipefail # Solely output coloration if the command is not being piped. if [ -t 1 ]; then COLOR="all the time" else COLOR="auto" fi git department --all --color="$COLOR" --sort=authordate --format="%(coloration:blue)%(authordate:relative);%(coloration:crimson)%(authorname);%(coloration:white)%(coloration:daring)%(refname:quick)" "$@" | column -s ";" -t
Do not forget to avoid wasting this to a file and make it executable!
This does a number of issues:
- It solely outputs coloration when the script is being run straight from the CLI. This lets you use
git-branchesin different scripts. - It types the branches by after they have been authored. This places the newest branches on the backside.
- It permits you to cross extra arguments to the
departmentcommand utilizing the$@Bash variable. This can are available in helpful within themy-branchescommand we’ll add subsequent. - It provides some good formatting to your branches. For instance, this is the reason my
branchesoutput seems to be like in my dotfiles repo. This works through the use of a trick with thecolumncommand and changing semicolons within the output so the objects line up properly.
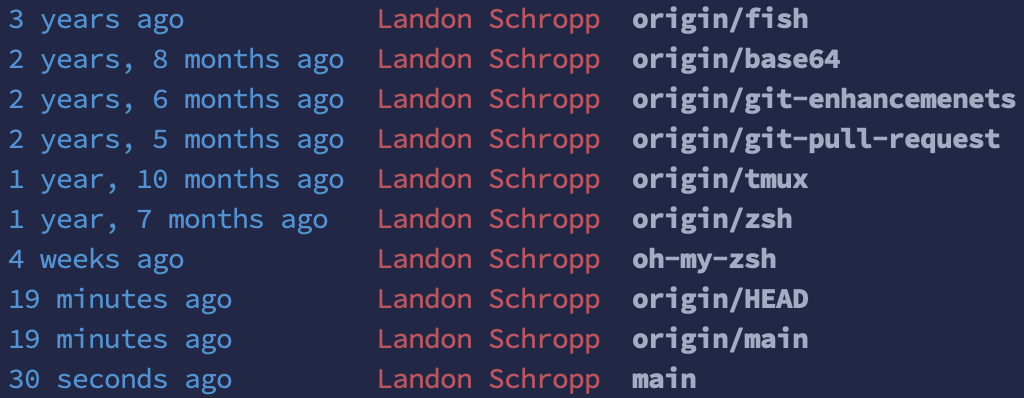
Add an alias for this command (and a brief alias in case you like brevity).
[alias] branches = "!$HOME/.dotfiles/bin/git/git-branches" bs = branches
You are all set! Now you can run git branches (or simply git bs) to see all off of the out there branches.
Listing My Branches
The branches command you simply added could be very useful, however if you’re working with a big workforce, it may be a ache to see everybody’s branches. I wish to create a second alias that solely contains my branches. You possibly can simply accomplish this with a brand new script.
#!/usr/bin/env bash set -euo pipefail # Solely output coloration if the command is not being piped. if [ -t 1 ]; then COLOR="all the time" else COLOR="auto" fi "$HOME/.dotfiles/bin/git/git-branches" --color="$COLOR" | grep "$(git config person.title)"
This script runs git-branches after which pipes the output via grep to filter it all the way down to the present person’s branches.
Create aliases for each of those instructions.
[alias] my-branches = "!git branches | grep -i '$()'" my-bs = my-branches
You may cut back the quick alias to git mbs, however I do not as a result of writing git my-bs makes me smile each time I run it.
Stash Staged
Git has a git stash command, which is beneficial for setting apart work for later. By default, it solely stashes tracked recordsdata. In case you have new recordsdata you wish to stash new recordsdata, it’s important to embody the --include-untracked flag, or use git stash --all.
What do you do in case you solely wish to stash some of your recordsdata? The built-in manner to do that is Git funky.
As an example you wish to stash the recordsdata apple and banana, however preserve cherry and date. To try this, you add the recordsdata you do not wish to stash to the index, after which run git stash --keep-index --include-untracked.
git add cherry date git stash --keep-index --include-untracked
That is unusual as a result of it is the precise reverse manner that git commit works. Plus, you now have a few recordsdata floating round in your index that you will have to run git restore on.
To repair this, let’s create a git stash-staged command.
#!/usr/bin/env bash set -euo pipefail git diff --staged --name-only | xargs git stash push "$@" --
That is it! This command makes use of git diff --staged --name-only to print out a listing of the entire recordsdata which can be within the index. Then, it pipes these arguments to xargs. xargs splits up the arguments by newlines and passes them to git stash --.
Add your alias, and also you’re completed!
Aliases
You certain have been writing plenty of aliases recently. Would not or not it’s good if there was a command we may run to record the entire aliases you have created? We are able to add an alias for that!
[alias] aliases = "config --get-regexp alias"
That is All For Now!
That is it! Hopefully, you have loved this text, and you may make good use of the aliases right here.
Do you might have a favourite Git alias? Let me learn about it down within the feedback!

About Landon Schropp
Landon is a developer, designer and entrepreneur primarily based in Kansas Metropolis. He is the creator of the Unraveling Flexbox. He is enthusiastic about constructing easy apps folks love to make use of.
[ad_2]
