[ad_1]
As a result of Rockset helps organizations obtain the info freshness and question speeds wanted for real-time analytics, we typically are requested about approaches to enhancing question pace in databases on the whole, and in common databases reminiscent of Snowflake, MongoDB, DynamoDB, MySQL and others. We flip to trade consultants to get their insights and we cross on their suggestions. On this case, the collection of two posts that comply with handle the best way to enhance question pace in Snowflake.
Each developer needs peak efficiency from their software program companies. In terms of Snowflake efficiency points, you might have determined that the occasional gradual question is simply one thing that you must dwell with, proper? Or possibly not. On this publish we’ll talk about why Snowflake queries are gradual and choices you must obtain higher Snowflake question efficiency.
It’s not all the time simple to inform why your Snowflake queries are working slowly, however earlier than you may repair the issue, you must know what’s occurring. Partially certainly one of this two-part collection, we’ll make it easier to diagnose why your Snowflake queries are executing slower than normal. In our second article, What Do I Do When My Snowflake Question Is Gradual? Half 2: Options, we have a look at the most effective choices for enhancing Snowflake question efficiency.
Diagnosing Queries in Snowflake
First, let’s unmask widespread misconceptions of why Snowflake queries are gradual. Your {hardware} and working system (OS) don’t play a task in execution pace as a result of Snowflake runs as a cloud service.
The community may very well be one purpose for gradual queries, nevertheless it’s not important sufficient to gradual execution on a regular basis. So, let’s dive into the opposite causes your queries is perhaps lagging.
Test the Data Schema
Briefly, the INFORMATION_SCHEMA is the blueprint for each database you create in Snowflake. It lets you view historic information on tables, warehouses, permissions, and queries.
You can’t manipulate its information as it’s read-only. Among the many principal capabilities within the INFORMATION_SCHEMA, you’ll find the QUERY_HISTORY and QUERY_HISTORY_BY_* tables. These tables assist uncover the causes of gradual Snowflake queries. You may see each of those tables in use beneath.
Take into account that this software solely returns information to which your Snowflake account has entry.
Test the Question Historical past Web page
Snowflake’s question historical past web page retrieves columns with worthwhile info. In our case, we get the next columns:
EXECUTION_STATUSshows the state of the question, whether or not it’s working, queued, blocked, or success.QUEUED_PROVISIONING_TIMEshows the time spent ready for the allocation of an acceptable warehouse.QUEUED_REPAIR_TIMEshows the time it takes to restore the warehouse.QUEUED_OVERLOAD_TIMEshows the time spent whereas an ongoing question is overloading the warehouse.
Overloading is the extra widespread phenomenon, and QUEUED_OVERLOAD_TIME serves as an important diagnosing issue.
Here’s a pattern question:
choose *
from desk(information_schema.query_history_by_session())
order by start_time;
This provides you the final 100 queries that Snowflake executed within the present session. You can even get the question historical past based mostly on the person and the warehouse as properly.
Test the Question Profile
Within the earlier part, we noticed what occurs when a number of queries are affected collectively. It’s equally essential to deal with the person queries. For that, use the question profile choice.
Yow will discover a question’s profile on Snowflake’s Historical past tab.
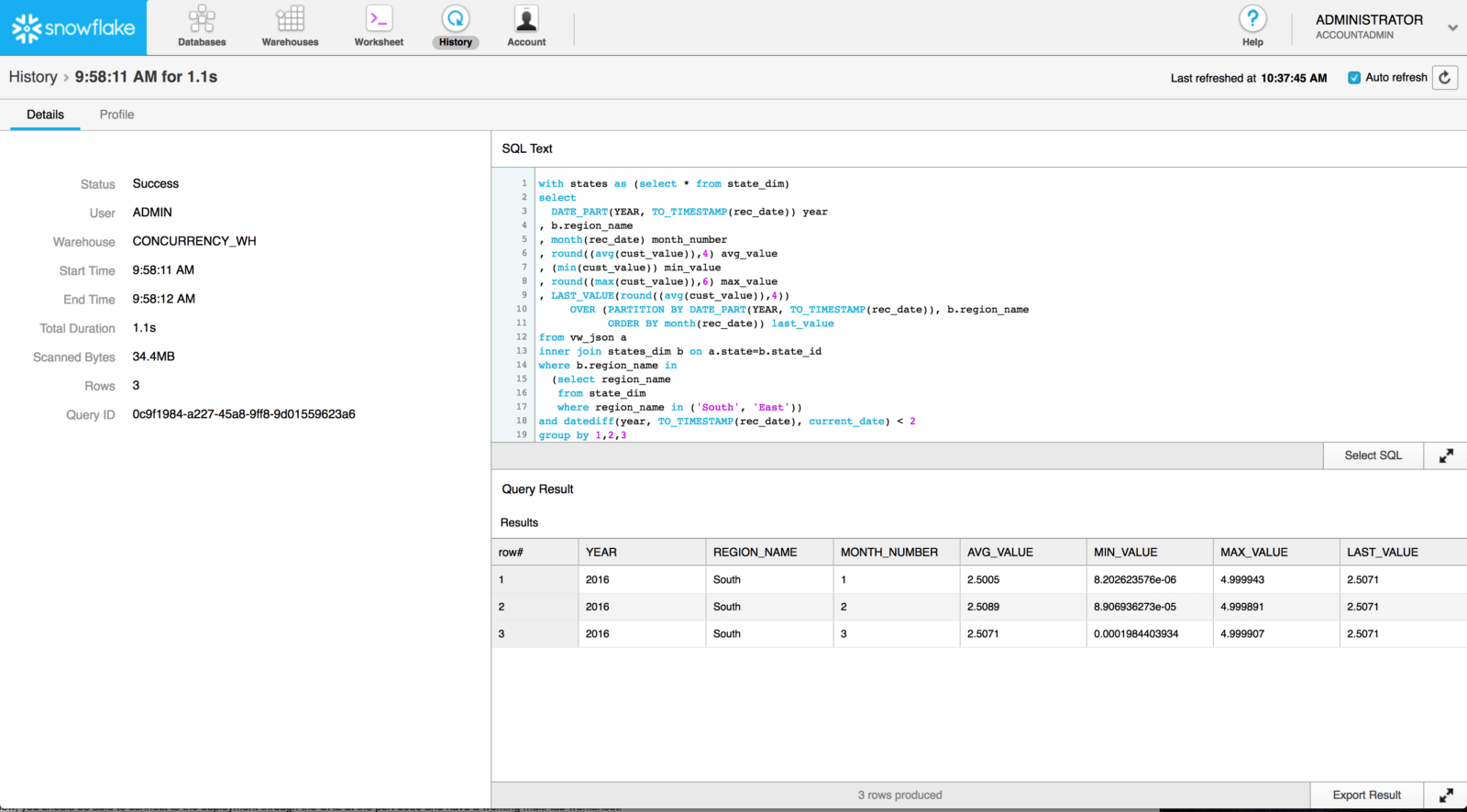
The question profile interface seems to be like a sophisticated flowchart with step-by-step question execution. You must focus primarily on the operator tree and nodes.
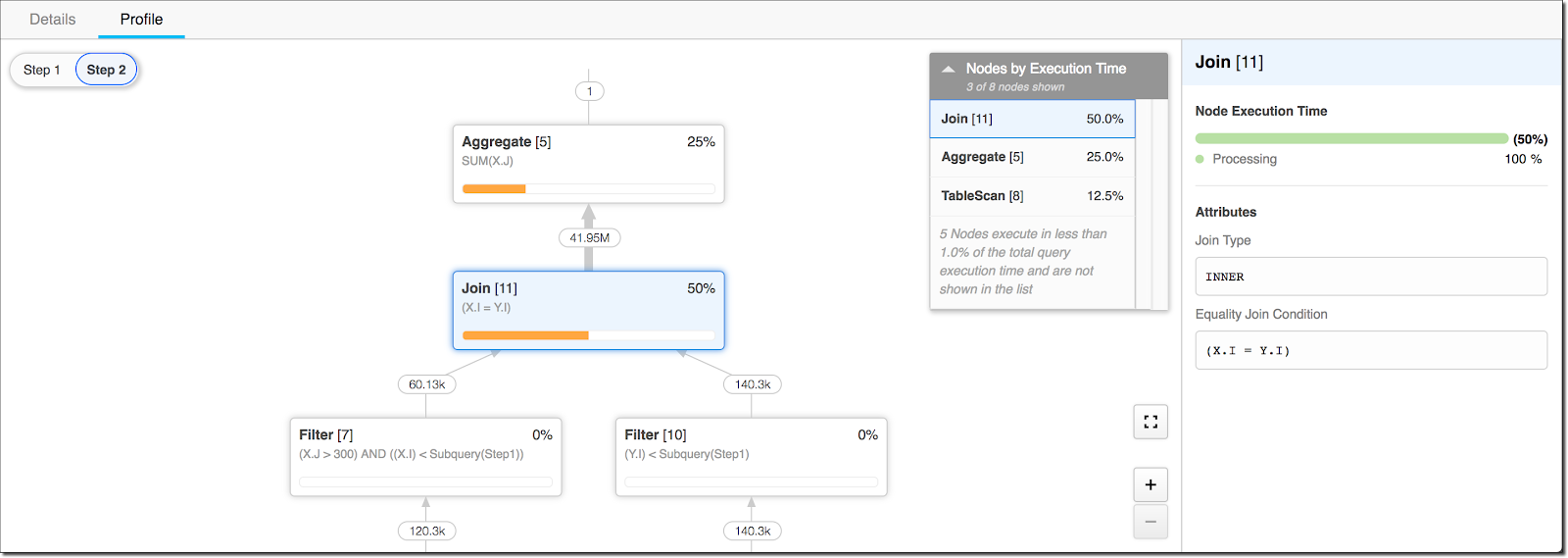
The operator nodes are unfold out based mostly on their execution time. Any operation that consumed over one p.c of the overall execution time seems within the operator tree.
The pane on the fitting aspect exhibits the question’s execution time and attributes. From there, you may work out which step took an excessive amount of time and slowed the question.
Test Your Caching
To execute a question and fetch the outcomes, it would take 500 milliseconds. In case you use that question continuously to fetch the identical outcomes, Snowflake offers you the choice to cache it so the following time it’s quicker than 500 milliseconds.
Snowflake caches information within the outcome cache. When it wants information, it checks the outcome cache first. If it doesn’t discover information, it checks the native exhausting drive. If it nonetheless doesn’t discover the info, it checks the distant storage.
Retrieving information from the outcome cache is quicker than from the exhausting drive or distant reminiscence. So, it’s best follow to make use of the outcome cache successfully. Knowledge stays within the outcome cache for twenty-four hours. After that, you must execute the question once more to get the info from the exhausting disk.
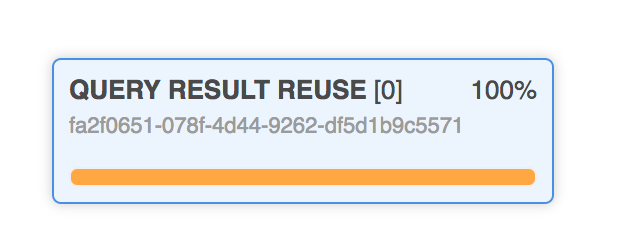
You possibly can try how successfully Snowflake used the outcome cache. When you execute the question utilizing Snowflake, verify the Question Profile tab.
You learn how a lot Snowflake used the cache on a tab like this.
Test Snowflake Be part of Efficiency
In case you expertise slowdowns throughout question execution, you need to evaluate the anticipated output to the precise outcome. You would have encountered a row explosion.
A row explosion is a question outcome that returns way more rows than anticipated. Subsequently, it takes way more time than anticipated. For instance, you would possibly anticipate an output of 4 million information, however the end result may very well be exponentially increased. This drawback happens with joins in your queries that mix rows from a number of tables. The be a part of order issues. You are able to do two issues: search for the be a part of situation you used, or use Snowflake’s optimizer to see the be a part of order.
A simple solution to decide whether or not that is the issue is to verify the question profile for be a part of operators that show extra rows within the output than within the enter hyperlinks. To keep away from a row explosion, make sure the question outcome doesn’t include extra rows than all its inputs mixed.
Much like the question sample, utilizing joins is within the palms of the developer. One factor is evident — dangerous joins lead to gradual Snowflake be a part of efficiency, and gradual queries.
Test for Disk Spilling
Accessing information from a distant drive consumes extra time than accessing it from an area drive or the outcome cache. However, when question outcomes don’t match on the native exhausting drive, Snowflake should use distant storage.
When information strikes to a distant exhausting drive, we name it disk spilling. Disk spilling is a typical reason behind gradual queries. You possibly can determine cases of disk spilling on the Question Profile tab. Check out “Bytes spilled to native storage.”
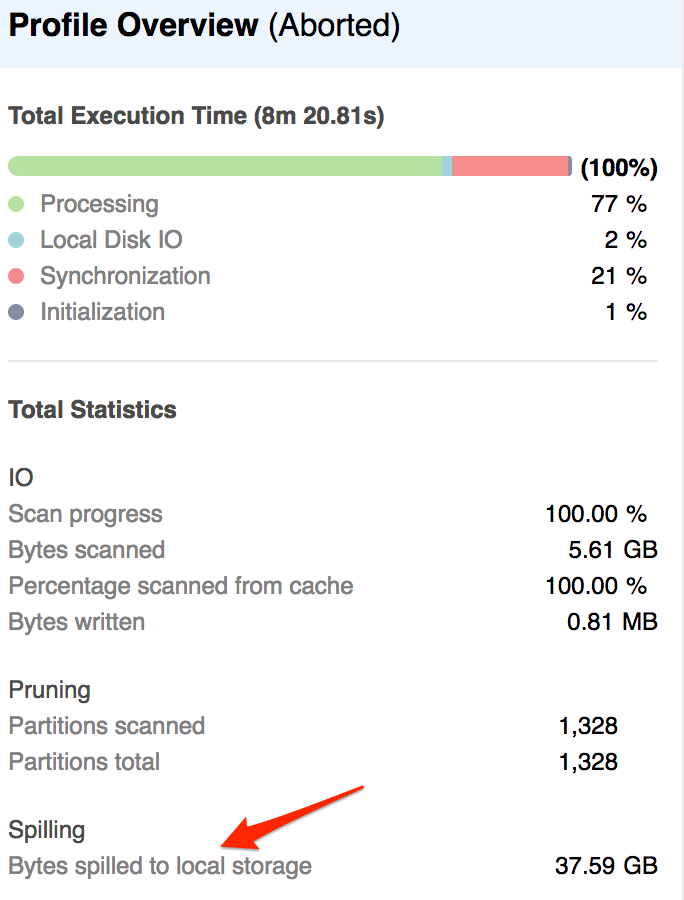
On this instance, the execution time is over eight minutes, out of which solely two p.c was for the native disk IO. Which means Snowflake didn’t entry the native disk to fetch information.
Test Queuing
The warehouse could also be busy executing different queries. Snowflake can’t begin incoming queries till satisfactory sources are free. In Snowflake, we name this queuing.
Queries are queued in order to not compromise Snowflake question efficiency. Queuing might occur as a result of:
- The warehouse you might be utilizing is overloaded.
- Queries in line are consuming the required computing sources.
- Queries occupy all of the cores within the warehouse.
You possibly can depend on the queue overload time as a transparent indicator. To verify this, have a look at the question historical past by executing the question beneath.
QUERY_HISTORY_BY_SESSION(
[ SESSION_ID => <constant_expr> ]
[, END_TIME_RANGE_START => <constant_expr> ]
[, END_TIME_RANGE_END => <constant_expr> ]
[, RESULT_LIMIT => <num> ] )
You possibly can decide how lengthy a question ought to sit within the queue earlier than Snowflake aborts it. To find out how lengthy a question ought to stay in line earlier than aborting it, set the worth of the STATEMENT_QUEUED_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDS column. The default is zero, and it will possibly take any quantity.
Analyze the Warehouse Load Chart
Snowflake presents charts to learn and interpret information. The warehouse load chart is a helpful software, however you want the MONITOR privilege to view it.
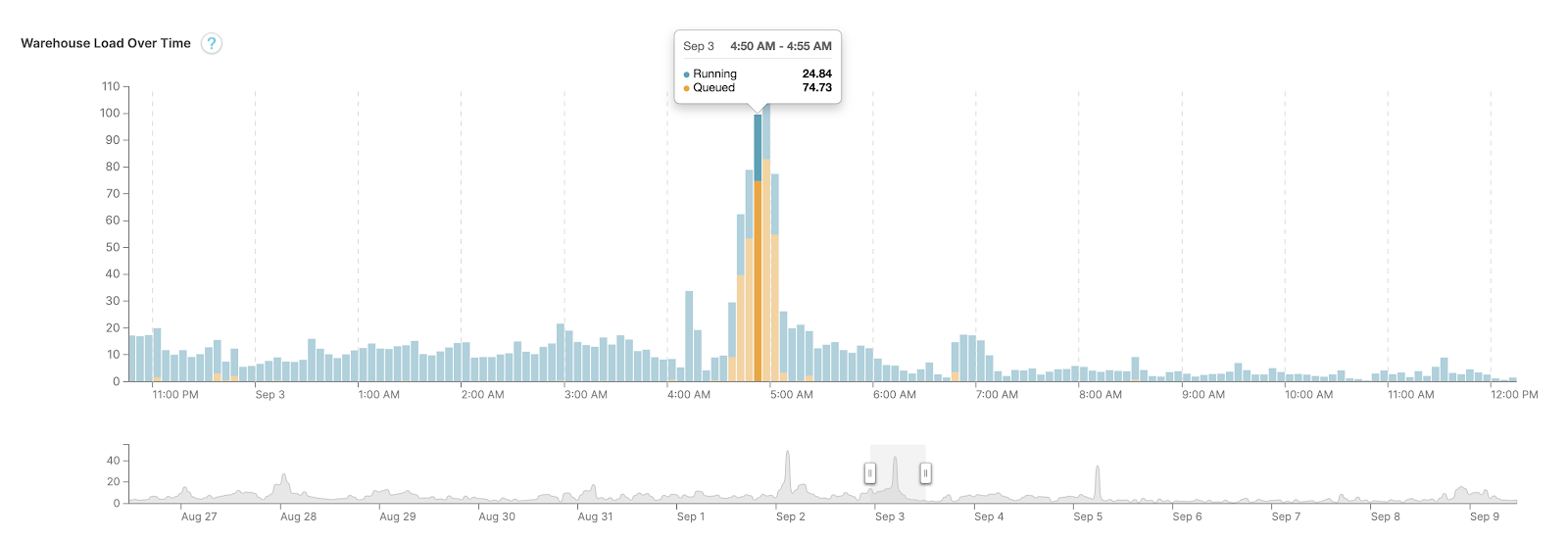
Right here is an instance chart for the previous 14 days. Whenever you hover over the bars, you discover two statistics:
- Load from working queries — from the queries which can be executing
- Load from queued queries — from all of the queries ready within the warehouse
The whole warehouse load is the sum of the working load and the queued load. When there isn’t any competition for sources, this sum is one. The extra the queued load, the longer it takes to your question to execute. Snowflake might have optimized the question, however it could take some time to execute as a result of a number of different queries have been forward of it within the queue.
Use the Warehouse Load Historical past
Yow will discover information on warehouse hundreds utilizing the WAREHOUSE_LOAD_HISTORY question.
Three parameters assist diagnose gradual queries:
AVG_RUNNING— the typical variety of queries executingAVG_QUEUED_LOAD— the typical variety of queries queued as a result of the warehouse is overloadedAVG_QUEUED_PROVISIONING— the typical variety of queries queued as a result of Snowflake is provisioning the warehouse
This question retrieves the load historical past of your warehouse for the previous hour:
use warehouse mywarehouse;
choose *
from
desk(information_schema.warehouse_load_history(date_range_start=>dateadd
('hour',-1,current_timestamp())));
Use the Most Concurrency Degree
Each Snowflake warehouse has a restricted quantity of computing energy. Basically, the bigger (and costlier) your Snowflake plan, the extra computing horsepower it has.
A Snowflake warehouse’s MAX_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL setting determines what number of queries are allowed to run in parallel. Basically, the extra queries working concurrently, the slower every of them. But when your warehouse’s concurrency stage is simply too low, it would trigger the notion that queries are gradual.
If there are queries that Snowflake cannot instantly execute as a result of there are too many concurrent queries working, they find yourself within the question queue to attend their flip. If a question stays within the line for a very long time, the person who ran the question might imagine the question itself is gradual. And if a question stays queued for too lengthy, it could be aborted earlier than it even executes.
Subsequent Steps for Enhancing Snowflake Question Efficiency
Your Snowflake question might run slowly for numerous causes. Caching is efficient however doesn’t occur for all of your queries. Test your joins, verify for disk spilling, and verify to see in case your queries are spending time caught within the question queue.
When investigating gradual Snowflake question efficiency, the question historical past web page, warehouse loading chart, and question profile all supply worthwhile information, providing you with perception into what’s going on.
Now that you simply perceive why your Snowflake question efficiency might not be all that you really want it to be, you may slender down potential culprits. The next step is to get your palms soiled and repair them.
Do not miss the second a part of this collection, What Do I Do When My Snowflake Question Is Gradual? Half 2: Options, for tips about optimizing your Snowflake queries and different selections you may make if real-time question efficiency is a precedence for you.
Rockset is the real-time analytics database within the cloud for contemporary information groups. Get quicker analytics on more energizing information, at decrease prices, by exploiting indexing over brute-force scanning.
[ad_2]

